Sexually transmitted diseases, often referred to as STIs, are infections that are typically transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact. These infections are quite common and can be effectively treated, especially when diagnosed in the early stages.
What Are Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STIs)?
Sexually transmitted diseases are infections that are transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact. This contact usually involves the female and male genitalia, but in some cases, these diseases can spread through other forms of physical contact. This is because certain sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes and HPV, can be spread through skin-to-skin contact.
Types of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
There are over twenty types of sexually transmitted infections, and some of these types are detailed below:
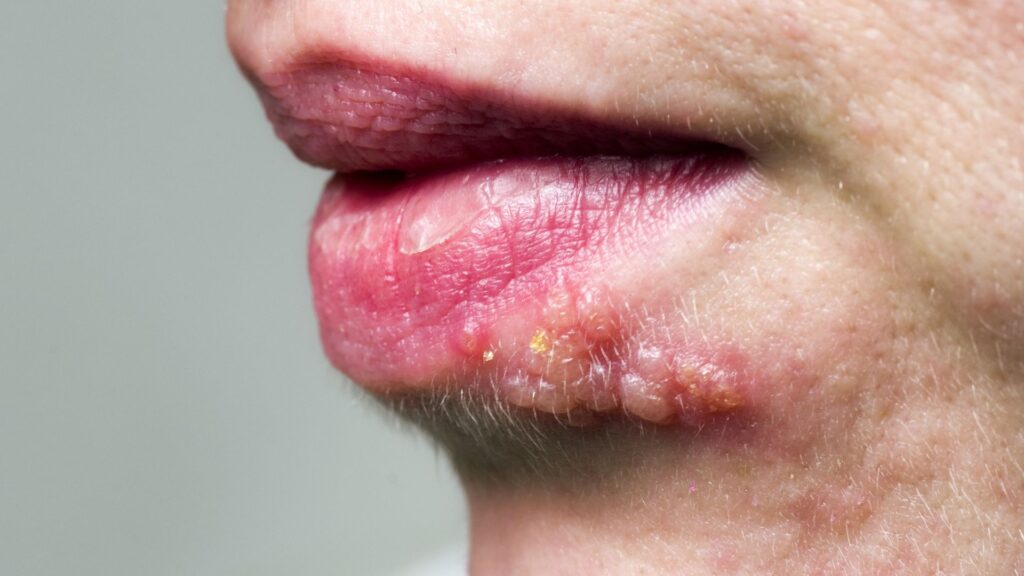
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can affect the skin, cervix, genitals, and other parts of the body. It often manifests around the mouth and can be transmitted through saliva or contact with a herpes-related sore. It can also be transmitted to the genital areas during oral sex. Herpes can be spread by touching an infected area and then touching another part of the body.
Once infected, the virus remains in the body, leading to symptoms like blisters around the mouth, urethra, or genitals. These blisters can burst, causing painful sores that take a week or more to heal. Having herpes can increase the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV. Herpes can be asymptomatic, but it can still be transmitted to others. Currently, there is no cure, but medications can help manage symptoms, and daily antiviral medications can reduce the risk of transmission.
It’s important to note that condom use does not provide complete protection against herpes.
Taking care of your health is crucial to avoid complications in the future. For expert guidance, please reach out.
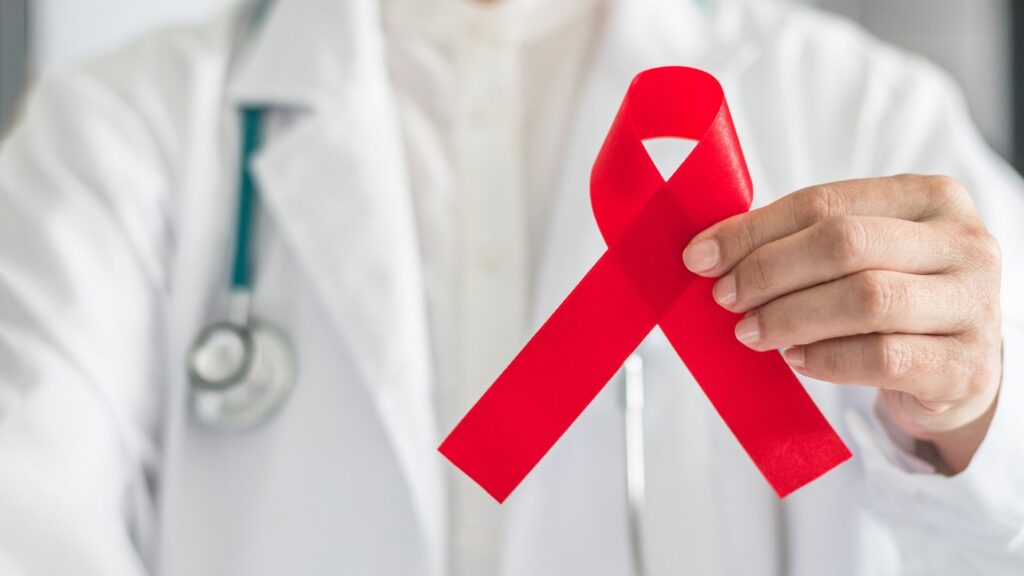

HIV
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system and can be transmitted through sexual contact and other means. It makes a person more susceptible to various infections and increases the risk of other sexually transmitted diseases. When a person becomes infected with HIV, the virus is present in their body fluids, such as semen, blood, breast milk, vaginal, and rectal fluids.
If these fluids enter another person’s body, they can become infected with HIV. People with HIV should seek treatment from qualified medical professionals. Here are some ways to prevent HIV transmission:
- Use a condom or other forms of contraception during vaginal or anal sex.
- Consider pre-exposure prophylaxis, a medication that helps prevent HIV in individuals at risk.
- Ensure safe disposal of syringes and handle sharp tools with care.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a common infection that can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be passed to a baby during childbirth. Chlamydia often presents with no symptoms, but if left untreated, it can lead to infertility and other complications. Fortunately, it is easily treatable with prompt intervention. If symptoms do occur, they may include changes in vaginal discharge and burning or pain during urination.
Chlamydia can also affect the urinary tract if sexual intercourse involves the urinary tract or if it spreads from another part of the body. Symptoms typically appear one to three weeks after intercourse. If you experience symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a doctor promptly to prevent further infection.
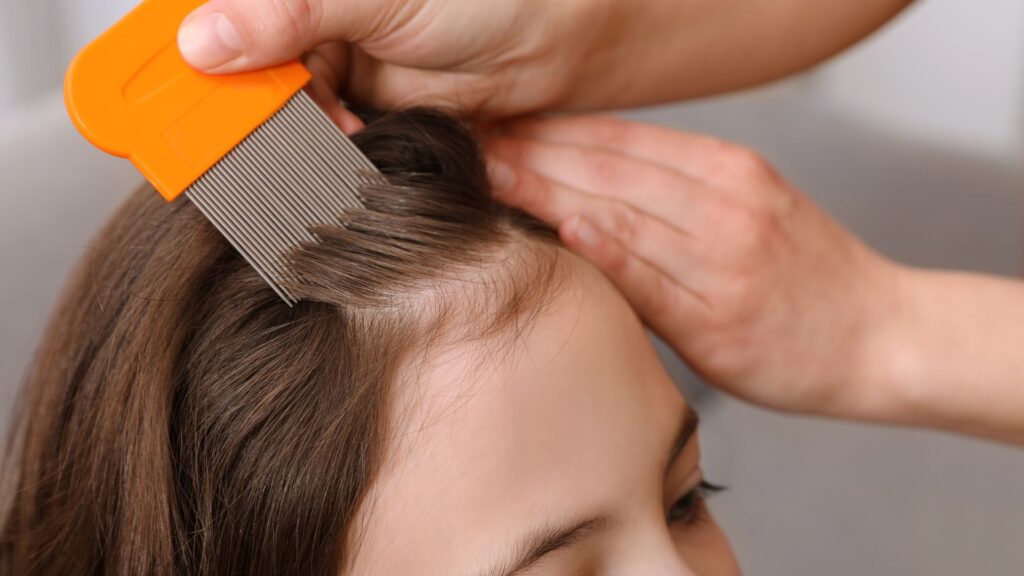
Crabs or Pubic Lice
Crabs, also known as pubic lice, are usually found in pubic hair but can affect other areas like the armpits, mustache, beard, eyelashes, or eyebrow hair. They are very small and hard to see, but they cause itching in the affected areas. Pubic lice can be transmitted through close physical and sexual contact, as well as shared towels or bedclothes.
To remove pubic lice in the genital area, a one percent permethrin solution or a similar product can be used. However, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist before using any new product.
For any skin-related concerns, feel free to reach out for assistance.
Causes and Effects of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Most STIs affect both men and women, but they can lead to more severe health problems in women. If a pregnant woman has an STI, it can result in serious health issues for the baby. If you are experiencing STI symptoms during pregnancy, please consult a reliable and expert gynecologist.
Treatment and Tips for Sexually Transmitted Diseases
To confirm the presence of an infection, a doctor may perform a sexually transmitted disease test and recommend the most appropriate treatment. Bacterial infections can be treated with antibiotics, but some STIs may develop antibiotic resistance if not fully treated. Completing the antibiotic treatment is crucial to prevent a resurgence of the infection. Vaccines are also available to protect against HPV and hepatitis B.
Your health is important, and seeking prompt medical attention is the key to managing sexually transmitted diseases.
In conclusion,
understanding the critical aspects of sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) is vital for our overall well-being and the well-being of our partners. These infections, commonly referred to as STIs, are primarily transmitted through sexual contact, and their prevalence underscores the importance of awareness and proactive measures.
While a wide variety of STIs exists, including genital herpes, HIV, chlamydia, and pubic lice, each demands unique attention and care. Regular testing, safe sexual practices, and open communication with healthcare professionals are key components of prevention and management. It’s worth noting that some STIs, like HIV, can lead to other health complications and should be treated with urgency.
By taking responsible steps, such as practicing safe sex, undergoing appropriate testing, and seeking timely medical intervention, we can significantly reduce the risk of STIs and their potential consequences. Additionally, vaccines are available for certain infections, further emphasizing the importance of vaccination as a preventive measure.
In the realm of sexual health, knowledge is empowerment. The more we understand and actively address the challenges posed by STIs, the better equipped we are to protect ourselves and our partners. It’s essential to remember that early detection, proper treatment, and responsible behavior can make a profound difference in our individual well-being and in our collective efforts to minimize the impact of these diseases. Together, we can work towards a healthier and safer future.



